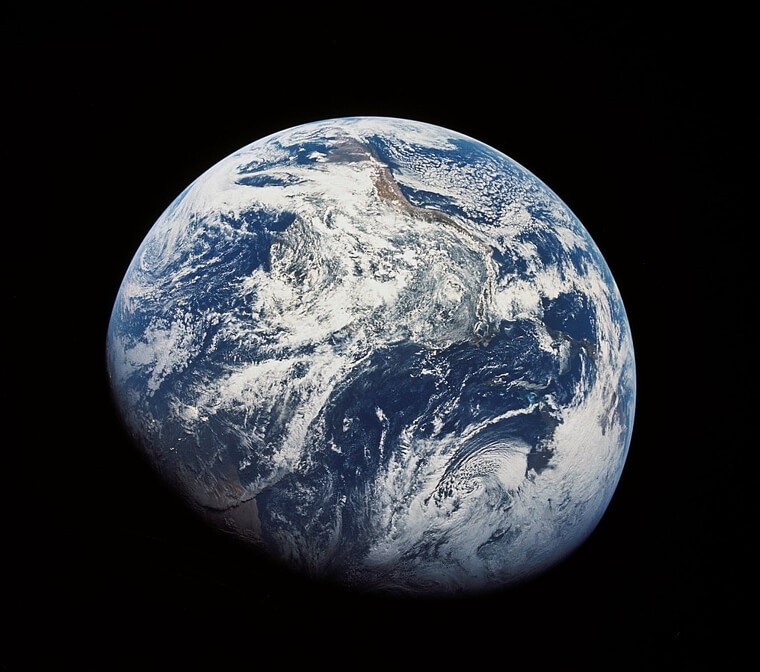
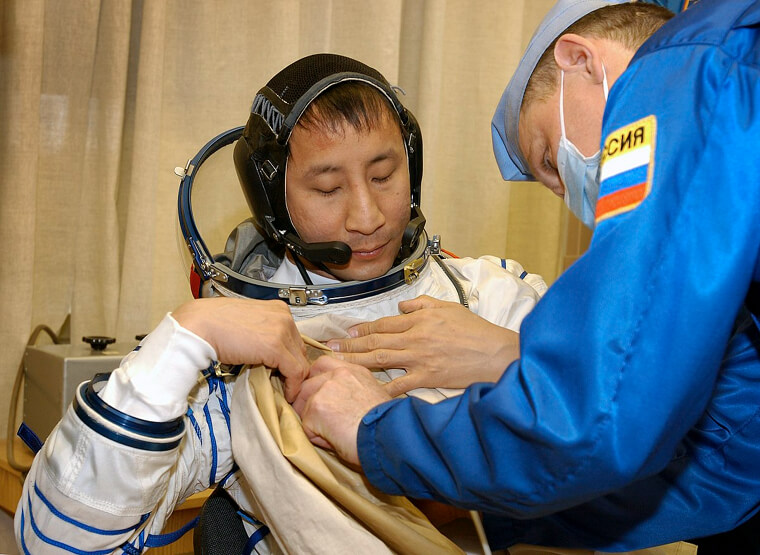
Astronauts Experience Cognitive Issues After Returning to Earth
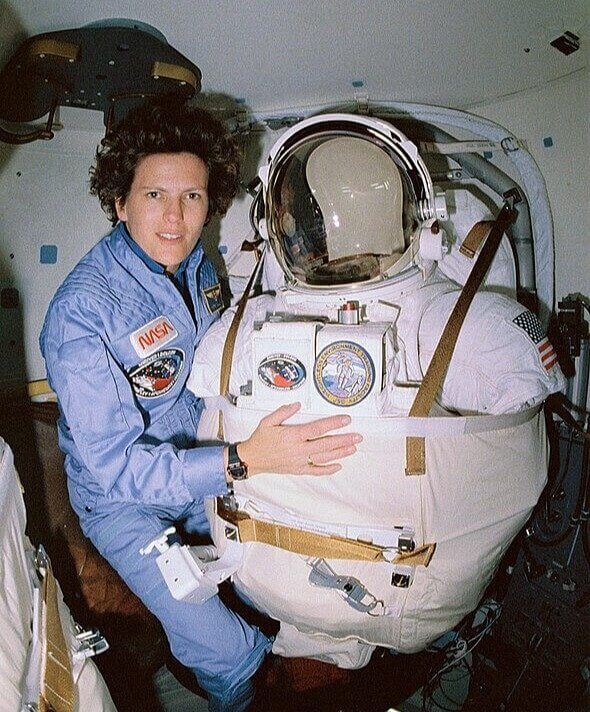
Embarking on a space journey isn't just a cosmic adventure; it's a formidable test for the human body. While symptoms reported by astronauts are typically temporary, readjusting to Earth isn't a walk in the park. The substantial stress of returning and adapting to normal gravity exacts its toll, often manifesting as joint pain and the infamous "space fog." Short-term memory lapses, delayed reactions, attention deficits, and confusion become common hurdles.
Far from the glamorized notion of space exploration, this reality check underscores the physical and cognitive challenges astronauts grapple with upon their return to our home planet.
Space Travel Can Change Your Eyesight
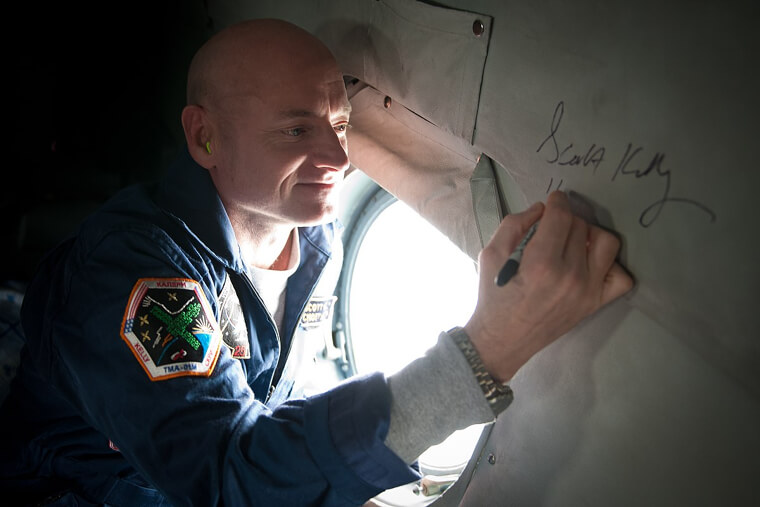
Journeying through space isn't just a cosmic adventure; it can apparently change one's eyesight. A study comparing astronaut Scott Kelly to his twin, Mark, revealed a thickening of Scott's retina—a crucial part of the eye that affects vision. Such structural changes can result in far-sightedness. Beyond retinal adjustments, astronauts have experienced optic nerve swelling and folds in the choroid, the tissue linking the retina and sclera. These brave astronauts really undergo tons of physical stress to travel in space.
The microgravity environment of space prompts intriguing changes in astronauts' eyes, shedding light on the intricate adaptations required for vision in the cosmos.
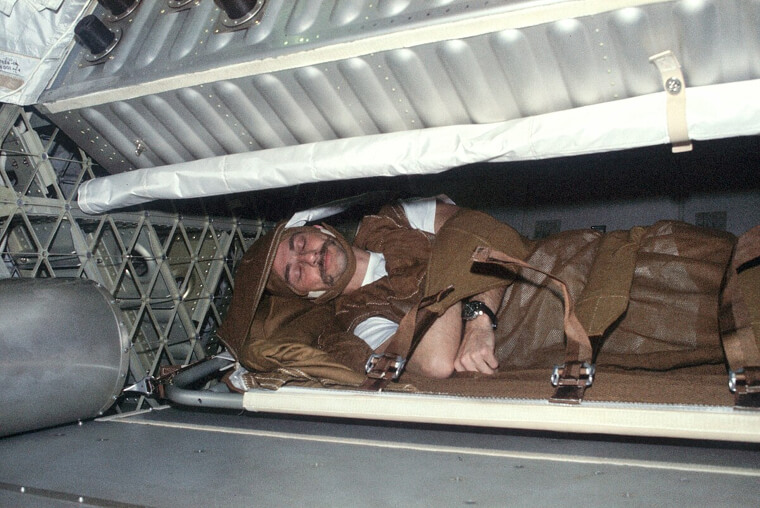
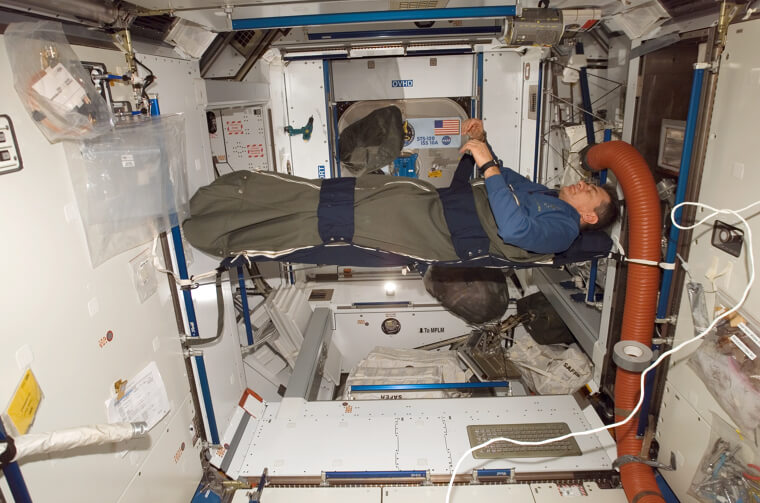
Astronauts Must Lock Themselves Into a Sleeping Bag so They Don't Float Away
Surviving space travel presents formidable obstacles, with zero gravity and heightened radiation impacting the body. Yet, even upon reaching the space station, a good night's sleep proves elusive for astronauts. In microgravity, sleeping becomes a unique challenge, requiring astronauts to secure themselves in sleeping bags to prevent floating away. Adding to the complexity, space stations can be surprisingly noisy, and at higher altitudes, cosmic rays may streak across astronauts' vision, disrupting their sleep.
As an astronaut, you must have extreme levels of adaptability for even the most basic activities in space; literally locking yourself into place just for a restful night.
Tracking a Black Hole's Speed in the Milky Way
Hold onto your hats—a black hole is racing through our Milky Way at 250,000 miles per hour! These cosmic vacuum cleaners, born from exploding stars, devour everything in their path. Hints about them come from space discoveries, like the Hubble Telescope. But what's so shocking that scientists have recently discovered? A star is circling our Milky Way's black hole. By watching this star's movements, scientists can figure out where the black hole is heading and how fast.
It's like solving a space mystery right in our galaxy, giving us a front-row seat to the dynamic journey of a high-speed black hole here in our own galaxy!
Your DNA Changes From Space Travel
Embarking on the cosmic journey, astronauts expose themselves to a unique set of conditions, prompting the question: Could space travel reshape human DNA? Astronaut Scott Kelly's unprecedented opportunity for research arose from his nearly identical twin brother, offering a comparative study. Upon Kelly's return from space, scientists discovered significant changes: DNA damage, altered gene expression, and abnormalities in chromosomes. The examination extended beyond genetic alterations, revealing thickening in his retina, shifts in the gut microbiome, and changes in the carotid artery.
This groundbreaking study unveils the multifaceted impact of space travel on human biology, shedding light on the intricate interplay between outer space and our genetic blueprint.
The Milky Way Is on Its Way to Collide With a Nearby Galaxy
Forget what we thought about the Milky Way just chilling in space! Recent findings reveal our home galaxy is on the move, and it's all thanks to a neighboring galaxy, the Large Magellanic Cloud. This cosmic neighbor, armed with a black hole, is tugging the Milky Way at an incredible 71,600 miles per hour, causing a bit of a galactic deformation. Experts theorize that in about 2.4 billion years, the Milky Way will collide with the Large Magellanic Cloud.
This collision might awaken our galaxy's dormant supermassive black hole, making it bigger. The Milky Way's stellar halo will also grow, and some stars will be flung into space.
Gamma-Ray Bursts Have the Potential to Destroy Earth
Here's another mind-blowing space fact: When massive stars bid farewell, they create supernovas, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes. But here's the cosmic twist—this cosmic farewell triggers gamma-ray bursts, ultra-powerful explosions that could, theoretically, wipe out life on Earth if aimed our way. Lucky for us, these dazzling bursts mainly occur in distant galaxies, keeping us safe. Yet, the show doesn't end there! These bursts leave behind a long-lasting "afterglow" in various wavelengths.
Scientists can actually study these rays to understand where they come from and whether they pose any potential threats to our cosmic neighborhood.
This Is What Happens to Astronauts' Poop
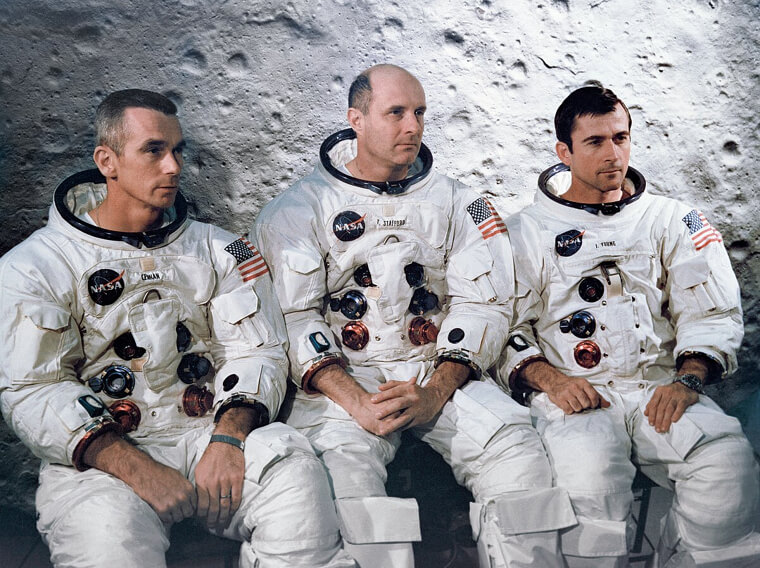
Navigating the challenges of waste disposal in space, NASA confronted a peculiar incident during the Apollo 10 mission. Commander Tom Stafford, in conversation with ground control, spotted a floating fecal surprise in the cabin, intensifying the quest for effective waste management. Typically, astronaut poop is either brought back to Earth for scientific study or subject to a unique process. It's vacuumed into airtight containers with additional waste and loaded onto cargo ships.
Then, the cargo ship is launched at Earth once it's full and eventually burns up in the Earth's atmosphere. So, if you ever see a shooting star, just think it could just be astronaut poo blown up.
Tackling Space Waste With Supercritical Water
Following the infamous "poop incident," NASA was determined to avoid another celestial mess. Learning from the Apollo 10 hiccup, they dedicated resources to revolutionizing space waste disposal. The breakthrough? Supercritical fluids, specifically high-pressure water, act like a superhero in breaking down waste efficiently. This innovation promises cleaner and more effective space missions. NASA's commitment to overcoming challenges showcases a dedication to progress, ensuring future cosmic ventures are not only safer but also environmentally responsible.
Their clever solution marks a significant step forward, demonstrating NASA's ongoing efforts to improve space exploration. We could've never guessed poop would be such an issue!
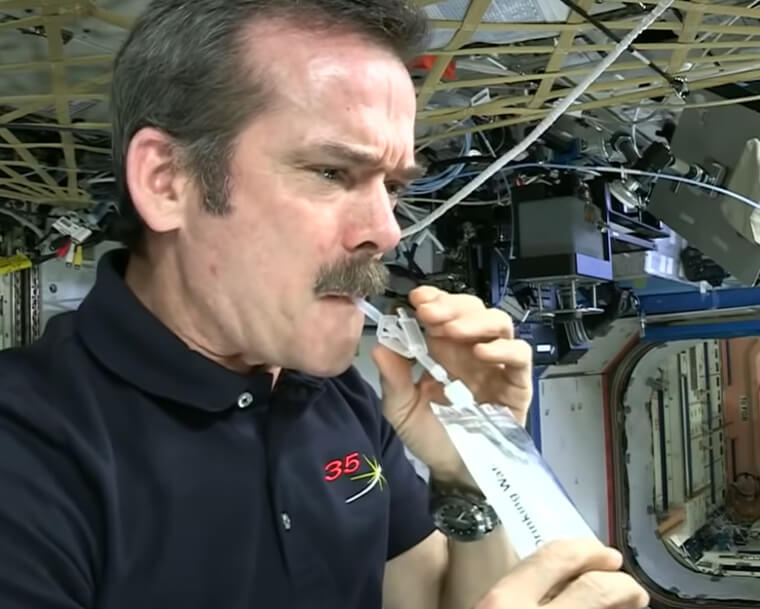
Astronauts Can Drink Their Own Pee to Stay Hydrated
In the vast expanse of outer space, transporting water presents a significant challenge due to its density. The International Space Station tackles this hurdle by implementing a unique recycling system that includes sweat, exhalations, and, yes, even urine. Astronauts find themselves sipping on purified pee, a testament to the rigorous processes involved in ensuring its safety. While it might not mimic the freshness of spring water, this innovative approach stands as a small but crucial price paid for space exploration.
It seems astronauts must creatively manage their water resources beyond Earth's boundaries. Who would've ever guessed this?
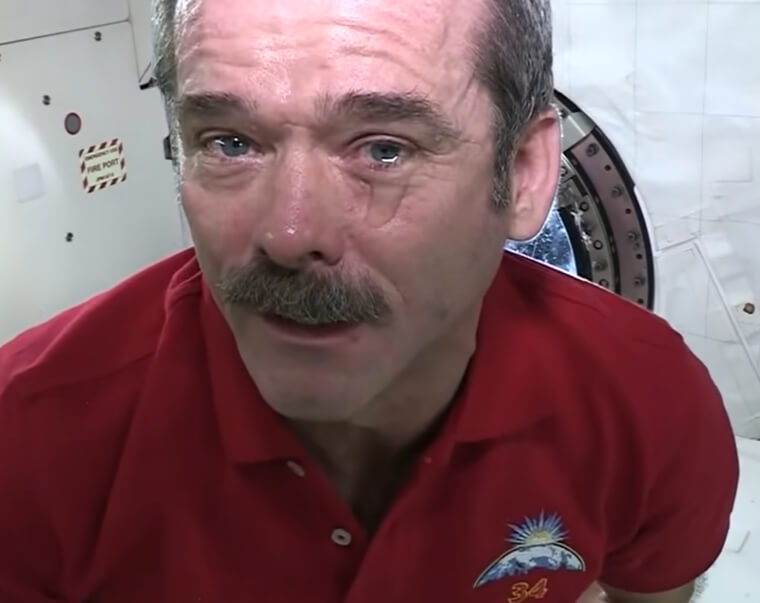
Tears Can't Fall in Space Because of Zero Gravity
Astronauts in space encounter a distinctive challenge when shedding tears due to the absence of gravity. Unlike on Earth, where tears naturally flow downward, zero gravity transforms the experience entirely. In this weightless environment, even the smallest movements evoke a significantly different sensation. The absence of gravity means tears don't fall; instead, they pool around the eyes, creating a disorienting puddle that blurs vision. Astronauts must rely on manually wiping away tears!
It's a process demanding caution to prevent tiny droplets from floating away. While people on Earth don't think twice about crying, astronauts in zero gravity have to be careful when this happens.
Astronauts Develop Alligator-Like Skin on Their Feet
Living aboard the International Space Station (ISS) is a unique experience, especially for astronauts' feet. In the absence of gravity, where floating replaces walking, an intriguing phenomenon unfolds. Astronauts have reported the disappearance of calluses after spending months in zero gravity. This unexpected change is attributed to reduced wear and tear on the soles compared to Earth. What's more, the tops of their feet undergo a peculiar transformation, becoming rougher due to the increased utilization in securing footholds.
Astronauts have to constantly use foot restraints that wrap around their feet and cause friction on the top of their feet. This results in almost alligator-like skin by the end of their missions in space.
The Truth About Sound in Space
The common understanding is that sound doesn't travel in space, but is the universe truly silent? While traditional sound waves can't be heard through space, there's an intriguing possibility involving interstellar gases. These gases have the potential to carry sound waves, but there's one catch. If these gases make sounds, we would never know. How could that be? Well, it's important to emphasize that any sounds that would occur in space would be beyond the reach of human hearing.
This seems like an abstract theory to comprehend, but advanced technology has actually captured the vibrations and sound waves in space that no human has heard with their own ears.
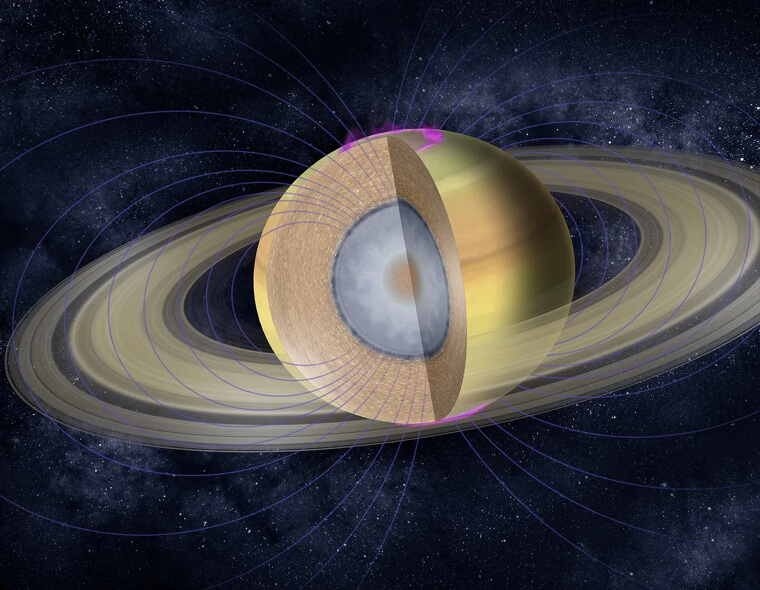
A Day on Saturn Lasts 10 Hours
Determining the length of a day on a planet might be something you've never thought of, or it might sound straightforward, but Saturn poses a unique challenge. With few identifiable features for marking a complete rotation and a magnetic field hindering electromagnetic measurements, scientists faced difficulties. However, the Cassini spacecraft emerged as the hero in this celestial mystery. Through its assistance, scientists unveiled the enigmatic duration of a Saturnian day: 10 hours, 33 minutes, and 38 seconds.
We didn't know there were so many complexities when it comes to measuring time. Can you even imagine living through a 10-hour day?
How Space Travel Slows Down Aging
Have you ever wondered if space travel could slow down the aging process? Well, Einstein had this fascinating idea called "space-time" in his Theory of Relativity. It suggests that the shape of space can influence how time passes. Surprisingly, astronauts on space stations seem to age a bit slower than those of us on Earth. It's like they have a small cosmic advantage that puts the brakes on their clocks.
But what does this even mean? Essentially, it means time moves slower as gravity increases. Forget fancy creams; perhaps all you need for a youthful touch is a ticket to ride into space!
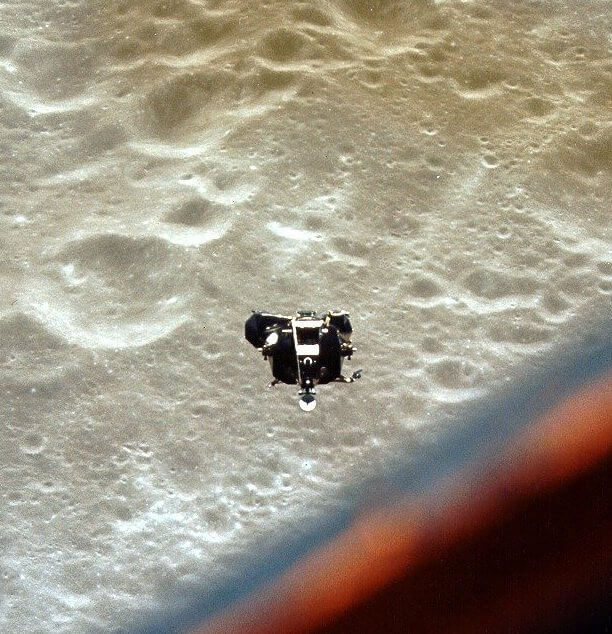
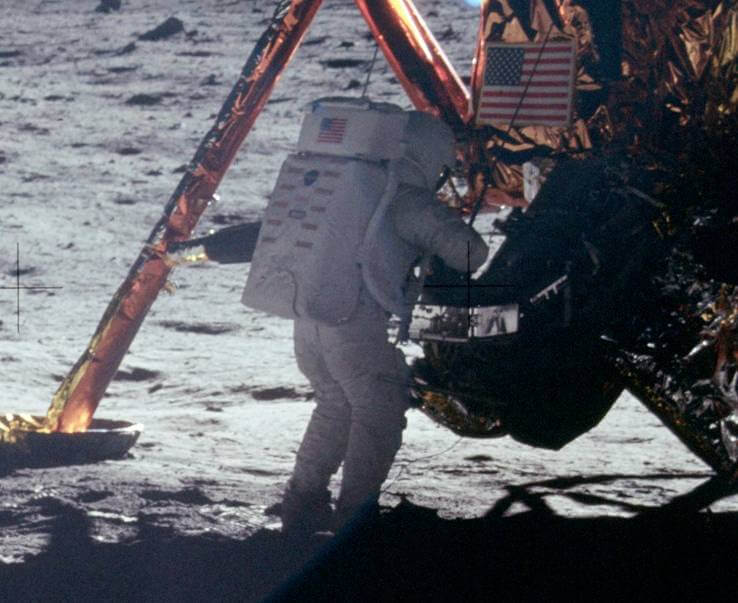
Neil Armstrong's Footprints Will Always Be on the Moon
In 1969, Neil Armstrong immortalized history with Apollo 11 and his famous words, "One small step for man, one giant leap for mankind." His footprints will forever be on the Moon's surface, preserved for millions of years! But how can his footprints stay on the surface that long and remain unchanged? Well, this is all due to the Moon's unique environment. It completely lacks wind and water, which, as a result, preserves the footsteps.
Unlike Earth, where elements erase such imprints, the Moon's tranquil landscape acts as a cosmic time capsule. Armstrong's footprints, frozen in lunar dust, endure as an extraordinary reminder of human exploration.
Chasing Another Planet That Could Be Similar to Earth, Gliese 581G
Our Earth is pretty special, but scientists are on the lookout for planets like ours. One candidate is Gliese 581g, about twenty light-years away. Sounds cool, right? Here's the catch: we're not sure if it's real. Imagine it like a potential Earth twin, possibly locked to its star, just like we are with the Sun. However, there's still a lot we don't know about this potential planet, especially about its atmosphere.
While we dream of finding another place like home, Gliese 581g adds a dash of excitement to the cosmic search for planets that could be our cosmic neighbors.
The Astounding Weight of the Sun
Ever wondered how much the Sun weighs? Get ready for a surprise—it's not just big; it's unbelievably heavy. Earth, our home, seems hefty at 5.972 x 10^24 kg, but it's like a feather compared to the Sun. The Sun's weight is a mind-boggling 1.989 × 10^30 kg, making up a whopping 99% of our solar system's total mass. To put it simply and give perspective, all the planets together contribute just 1%.
So, the Sun isn't just a shining ball in the sky; it's a heavyweight champ that weighs so much it's hard for us to comprehend.
How Scientists Measure the Temperature of Space
Delving into the universe's temperature might sound like rocket science, but it's not as tricky as it seems. Imagine the Big Bang as the cosmic starting point. Scientists, armed with the Big Bang Theory, explore how our universe works. One idea is that as the universe stretches out, it cools down. In 2013, researchers measured its temperature at –270.27 degrees Celsius, a bit chillier than before. But how do they come up with this number?
By examining radiation remnants from the Big Bang, scientists can infer the universe's temperature to be around 2.725 K. Surprisingly, this only represents less than 1% of the total energy in the universe anyway.
This Is What Outer Space Smells Like
Ever wondered about the scent of outer space? While our noses can't venture there, astronauts have shared intriguing experiences. Upon re-entering their spacecraft, they often detect the same odd odor. They have described it as a combination of rotten eggs and bitter almonds. What's even more fascinating is that compounds resembling the same scents have been identified on comets, only confirming astronauts' smells and providing a potential peek into space aromas.
Although the vacuum of space is likely odorless, the unique whiffs encountered by astronauts and the chemical clues found on celestial bodies add an intriguing layer to the ongoing quest to decode the fragrances of the cosmos.
Exploring 'The Big Rip' Theory of the Universe's End
Enter the realm of cosmological speculation with "The Big Rip," a captivating theory suggesting a unique perspective on the universe's end. The hypothesis proposes that, in approximately 22 billion years, the relentless expansion driven by dark energy will escalate to a point where even atoms undergo disintegration. This scenario challenges our understanding of cosmic destiny, but there are scientists who believe this theory wholeheartedly and genuinely believe this is how the world will end.
Though there are countless theories and facts about space that any ordinary person wouldn't know about, this list will help change that. Keep scrolling to discover things about space the experts finally shared.
The Ongoing Search for Alien Life
Let's talk aliens! While they're a staple in sci-fi, experts say finding extraterrestrial life isn't as wild as green humanoids. Our universe is massive, and scientists think there's a good chance at least one galaxy could have life-friendly conditions. We're not talking movie aliens, but the idea isn't far-fetched. Even though we haven't found concrete proof, the hunt for alien life continues. It's like a giant space mystery, and scientists are on the lookout.
NASA will keep searching for other life forms and has even mentioned that we can't overlook the presence of microbial life. Even if it's tiny, it's still a form of life.
The Potential Disaster of Solar Storms
Solar storms, like powerful energy bursts from the Sun filled with plasma and magnetic fields, threatened a global catastrophe in 2012. These storms, called coronal mass ejections, can wreak havoc on Earth's power grids and communication systems. Imagine a sudden blackout or disrupted internet and GPS! That year, an unusually strong solar storm came scarily close to colliding with our planet. Fortunately, we dodged the space bullet, avoiding potential chaos.
Solar storms can be dangerous because they interfere with radio frequencies and can increase levels of radiation, potentially harming people in aircrafts.
The Future Could Bring a Sky With No Stars
Picture a night sky, its beauty defined by the moon and stars; now envision it cloaked in absolute darkness billions of years from now. This cosmic metamorphosis isn't a scene from science fiction but a potential reality. Scientists theorize that if the universe's expansion persists, galaxies could drift so far apart that only complete darkness exists: no glimmer, no stars. This seems impossible, right? Well, according to experts, it's likely to occur.
While it would happen so far in the future that we wouldn't even exist, it is still very possible!
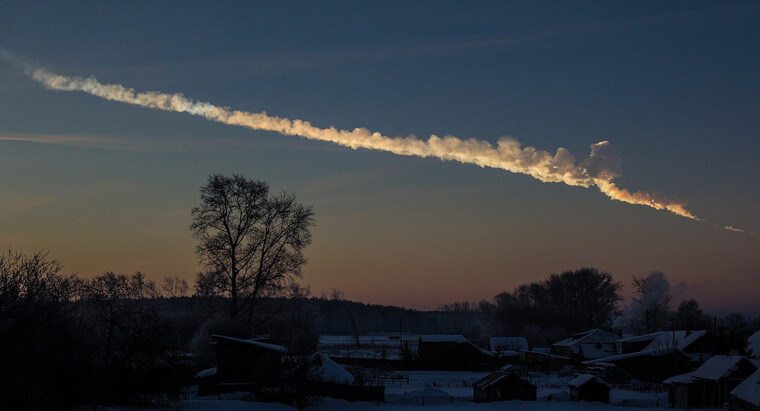
The Huge Meteor That Hit Russia
Scientists claim it's common for meteors to fall on Earth, but they are usually the size of pebbles. However, one day in 2013, Chelyabinsk, Russia, experienced an unexpected visit from a meteor that defied conventional detection. Unlike typical meteors, this one approached from a direction near the Sun, eluding our tracking systems. The surprise impact caused significant disruption, with around 1,500 people injured, primarily due to how powerful the shock waves were.
Shattered windows and damaged buildings left the town in disarray, prompting a reevaluation of our meteor tracking capabilities.
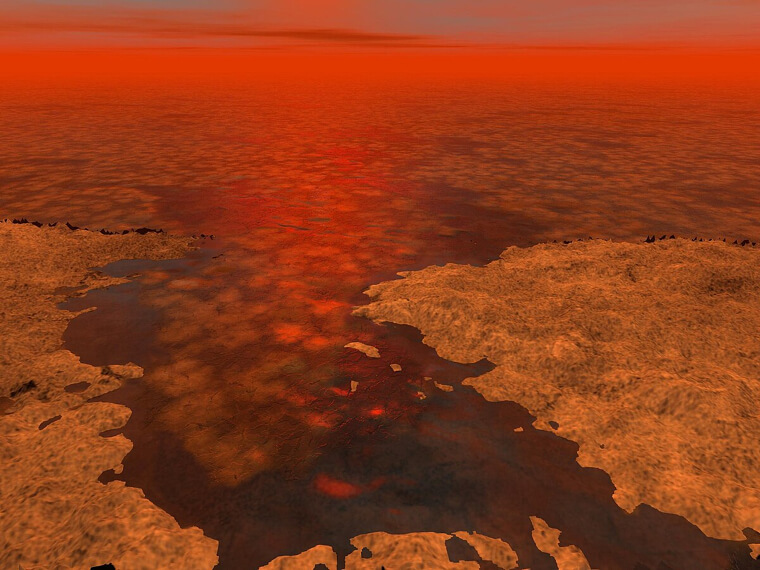
Scientists Discovered Methane Lakes on Saturn's Moon
Saturn's moon, Titan, isn't your typical moon. It has lakes, but not of water—these are filled with liquid methane! Discovered in 2007 by the Cassini mission, these lakes were tricky to spot at first because they don't reflect much light. Smart imaging techniques finally revealed them, showing these expansive, smooth areas up in Titan's north. Picture it like Titan's version of lakes, just with a methane twist. This was truly a shocking scientific discovery.
And get this: there are clouds of methane and moisture, suggesting Titan has an incredible cycle of evaporation and condensation.
It Snows at Night on Mars
Have you ever imagined snow falling on Mars? Well, believe it or not, it could be happening as we speak! Mars, our cosmic next-door neighbor, has become the focus of space exploration, with two NASA rovers diligently exploring its surface and sending back valuable data. Although Mars was a watery and warmer world in its distant past, it's very different today. Experts have shared that, more recently, the atmosphere has thinned and holds no liquid water.
The temperature dramatically drops in the evenings, and there are snowstorms. It was not what we quite expected from a red, fiery-looking planet.
When Galaxies Devour Each Other
Galaxies, those stunning cosmic wonders, sometimes engage in a phenomenon called "galactic cannibalism." Picture this: larger galaxies gobbling up smaller ones, creating radiant trails of material. It's like a cosmic dinner! Quasars, the giants of energy emission, partially thrive by consuming smaller systems. But, this celestial feasting comes with consequences. When galaxies hoard too much, they expel it, stalling new star births and eventually shutting down the galaxy. Sounds complicated, right?
Who would have thought that behind those amazing galaxy photos, there's a hidden reality of celestial feasts? These cosmic events aren't just captivating views; they have the power to completely transform a galaxy and sometimes even pose risks.
We Live Inside the Sun's Protective Bubble
Ever wondered where exactly Earth sits in relation to the Sun? We're not exactly in its atmosphere, but we do live within its heliosphere, which is a vast magnetic bubble full of solar winds. It's like a giant shield around all the planets in our solar system. Think of it as our galactic neighborhood's invisible fence. Initially thought to be a bubble, recent spacecraft observations showed it's more like a protective sphere.
So, while we're not hanging out in the Sun's atmosphere, our home planet enjoys the cozy embrace of its heliospheric shield, making our cosmic corner quite intriguing!
Understanding Cold Welding in Space
Delving into the realm of space engineering, there's a fact that most people have never heard of. There's a way to make metal stick together without melting it, and it's called "cold" or "contact" welding. Believe it or not, this technique isn't just some space-age idea; it's a real thing used in space and right here on Earth! The scientific rationale lies in the unique vacuum environment of space, facilitating the effortless bonding of similar metal surfaces.
Surprisingly, this cold welding phenomenon isn't exclusive to space. We use this trick to create connections in everyday things like copper wires and even on teeny-tiny nanowires. Who knew metal fusion could be this fascinating?
Saturn's Iconic Rings Won't Last Forever
Saturn, our second-largest planet, wows us with its spectacular eight rings, a cosmic treasure trove of comets, asteroids, moons, ice, and dust. Despite their solid appearance, these rings are fast-moving fragments. Here's the cosmic twist: anything disrupting their path heads into Saturn's vaporizing clouds, signaling a future where these iconic rings will fade away. It's tough to picture Saturn without its rings, but in the vast universe, change is constant.
The eventual disappearance of Saturn's rings serves as a reminder that even the grandest celestial features have a dynamic and evolving role in the cosmic ballet.
The Unseen Velocity Beneath Our Feet
This is another fact that is hard to believe. The Earth is spinning at an unimaginable speed, and most of us don't even notice! While we go about our lives, the ground beneath us is hurtling through space at an incredible 67,000 miles per hour. That's faster than any human-made object can dream of achieving. Imagine, every moment, you're part of an invisible, high-speed journey, and yet, our daily lives remain seemingly unaffected.
Without noticing, we're in a cosmic race, zooming through space at Earth's super speed. We move through the cosmos without feeling the crazy speed of our planetary journey.
Rogue Planets Potentially Outnumber Stars in Our Galaxy
You know those points of light you see in space pictures? Well, they're not all stars. While there are trillions of stars in the universe, a groundbreaking theory suggests that free-roaming or rogue planets might outnumber them. What makes this mind-blowing is that these planets seem to wander solo without a planetary system. The theory proposes they were either never tied to a star or got ejected from their original design.
In our Milky Way alone, it's estimated there are nearly two rogue planets for every star. This revelation reshapes our understanding of the cosmic population and introduces us to the hidden majority of celestial nomads.
How Astronauts Sleep in Space
In space, the realm of zero gravity, bedtime for astronauts is no ordinary affair. Deprived of the luxury of simply settling into a bed, they've had to navigate the challenge with creativity. To address this, astronauts use specially designed sleeping bags that keep them securely strapped in. While it may not replicate the coziness of a traditional bed, it's the ingenious solution ensuring they don't float away during their zero-gravity slumber.
It's hard to imagine having to buckle yourself in when you sleep so you don't float away! But it's just a regular night for astronauts traveling out of our atmosphere.
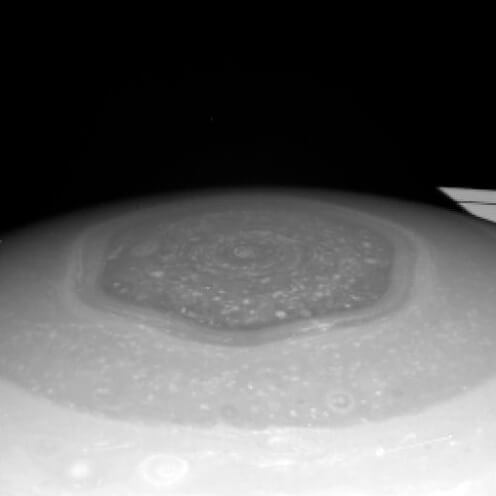
The Hexagon Mystery at the North Pole of Saturn
Another mystery about Saturn was revealed. A hexagon-shaped cloud was revealed by the Voyager mission in 1981, later transforming from blue to golden in 2006. Now, the big question: why does this odd hexagon exist? Experts from Oxford University have a theory—they think it's because the wind speeds at the center and edges are different. Similar shapes emerged when they conducted experiments with liquids by moving them at different speeds, but they're still not 100% sure.
While we're still piecing together the mystery of Saturn's hexagon, it adds another fascinating cosmic wonder to our solar system.